Trunnion Strength Evaluation
Trunnion Strength Evaluation
Published January 2026
Keywords
Share
References
Summary
The purpose of this file is to share information on trunnion supports. Sometimes in piping design, a trunnion is needed. When designing a trunnion, there are many factors to consider and best practices to follow.
Project/Case Example
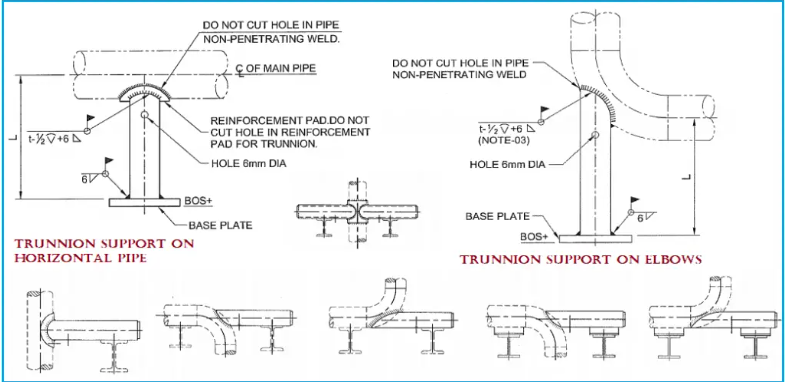
The piping industry uses trunnion supports, one of the most common types of pipes supports. The construction and erection of a pipe trunnion or dummy support are very easy because you have to simply weld a pipe (normally one or more sizes less than the parent pipe to which it is to be welded) with the parent pipe. Trunnion supports made of the same-sized pipe are typically avoided in construction because of challenges with profile cutting and welding.
The load-bearing capacity of trunnion supports is usually less and not as comparable to civil structural supports, if a structural support is welded to the pipe it should be reviewed by civil for loading capacity.
So, every pipe stress engineer must check the weld point from a failure viewpoint and investigate the ability to carry the piping load (mostly the tangential and longitudinal load and corresponding moment). The chances of weld failure increase with an increase in trunnion length or trunnion height. Usually, trunnions with a height of more than 900 mm are not suggested, the shorter the length of trunnion the better to reduce stress. Piping designers should follow JNE standard trunnion designs.
A variety of support configurations can be made by welding trunnion supports on pipes.
Codes and Standards
ASME B 31.3= Process Piping.
Solution/Best Practice
- Factors Affecting Load-Bearing Capability of Trunnions
The load-carrying capability of a trunnion mainly depends on the following factors.- Parent pipe and trunnion/dummy pipe diameter. With an increase in pipe size, the load-carrying capacity increases.
- Parent pipe thickness. With an increase in pipe thickness, the load-carrying capability increases.
- Parent pipe material. With an increase in parent pipe material allowable strength (Sh), the load-carrying capability increases.
- Design temperature. With a decrease in design temperature the load-carrying capability increases.
- Design pressure. With a decrease in design pressure the load-carrying capability increases.
- Trunnion/dummy pipe height. With a decrease in trunnion height the load-carrying capability increases.
- Reinforcement (RF) Pad thickness at the weld interface. Adding a reinforcement pad at the parent pipe and trunnion pipe increases the load-carrying capability of trunnions to a huge extent. However, adding RF pads at elbows is difficult to construct and hence suggested to avoid.
- Trunnion Calculation Method
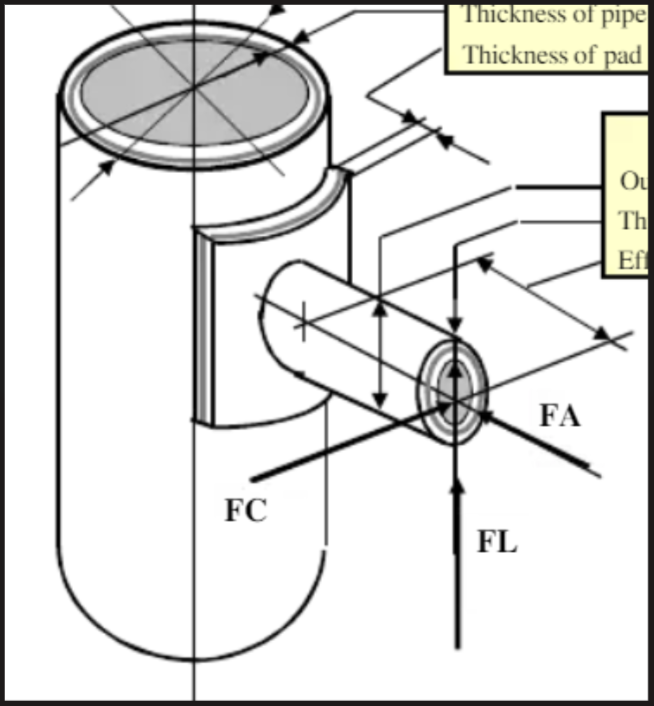
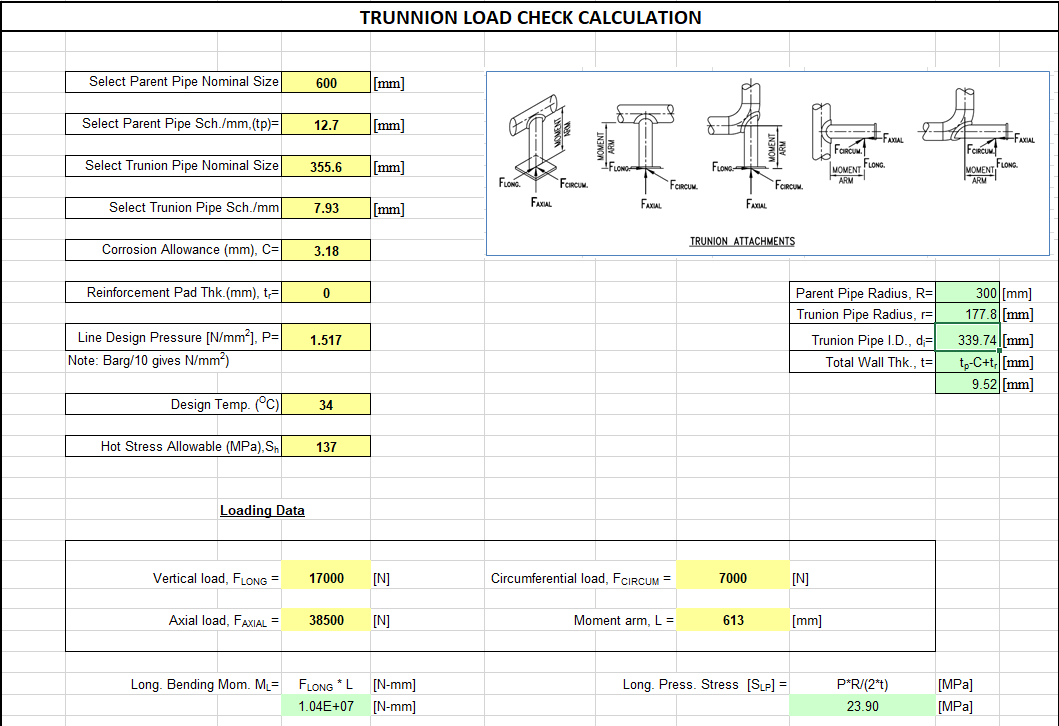
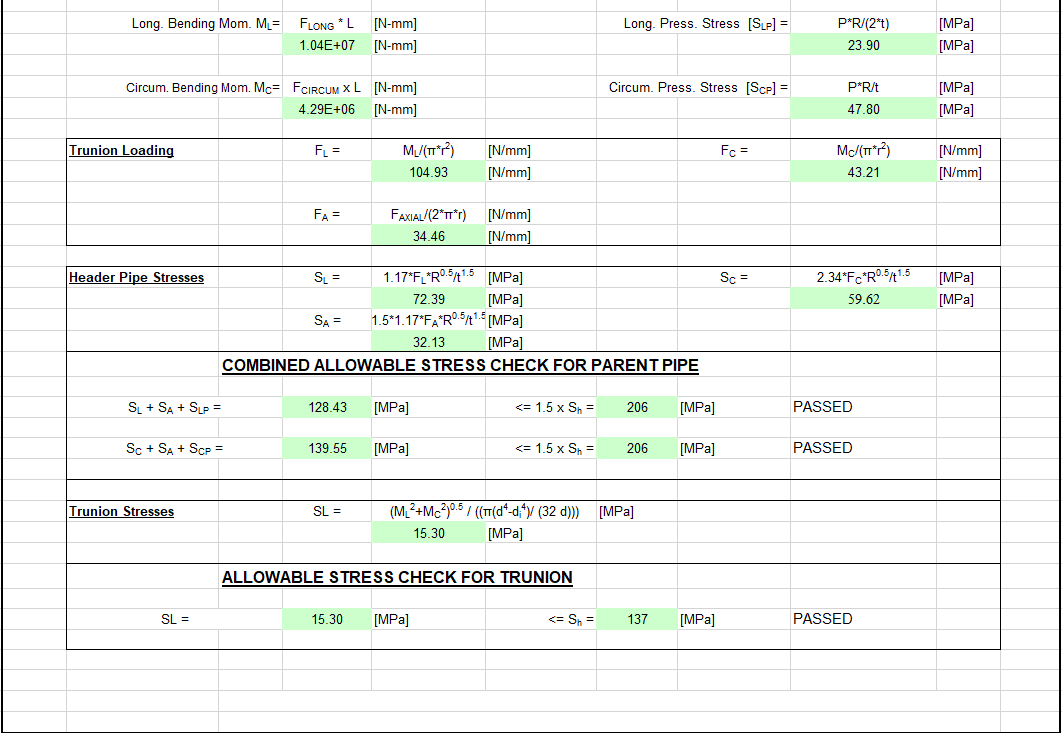
Kellogg Method of trunnion checking using an Excel spreadsheet is the most common among EPC organizations. The Kellogg Method considers stresses induced in the trunnion at the pipe wall.
- Inputs Required for Pipe Trunnion Calculation
- Pipe support loads from stress analysis software.
- Parent pipe OD and thickness.
- Pipe trunnion OD and thickness.
- Parent pipe corrosion allowance.
- Parent pipe material to get stress values.
- Pipe design temperature and pressure.
- Pipe trunnion height.
- RF pad thickness if required/provided.
- Kellogg Method Excel Sheet
- Options to Reduce Stresses While Trunnion Support Checking
- While reducing trunnions or dummies, it is found that a major chunk of trunnion supports fails due to circumferential loads. So, orient or place the trunnion in such a way that the circumferential force on the trunnion becomes less to permit/allow greater trunnion heights.
- Reducing the trunnion height or increasing the trunnion size also will reduce the calculated stresses.
- RF pads are required to be added to increase the junction thickness and thereby increase load-carrying capabilities which decrease stresses.
- Increasing the parent pipe diameter will also qualify the trunnions. However, increasing parent pipe size needs process confirmation.
As mentioned previously — if a trunnion is being used in the design and it does not follow standards and/or it is exposed to high loads, it should be reviewed in further detail through the Kellogg Method given potential failure that can occur.